SQL Server Tutorial: How to Create Table in SQL Server with Auto Increment, Primary Key and Foreign Key
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating, and retrieving database data. SQL stands for Structured Query language, pronounced as “S-Q-L”. It is a programming language with a standardized database and is used to modify the database and retrieve information from tables.
Modification of database tables, along with retrieving information subsets, can be done through SQL. Here we will learn how to create and alter tables in an SQL server using SQL queries. We also create here the primary key, the foreign key.
SQL is a standard language for storing, manipulating, and retrieving database data. SQL stands for Structured Query language, pronounced as “S-Q-L”. It is a programming language with a standardized database and is used to modify the database and retrieve information from tables.
Modification of database tables, along with retrieving information subsets, can be done through SQL. Here we will learn how to create and alter tables in an SQL server using SQL queries. We also create here the primary key, the foreign key.
We cover the below things,
Create SQL table
Alter SQL table
Primary key
Foreign Key
Let’s start with SQL
Firstly we have to create a database for using a table.
Use the following command to create the database.
Create database MySQLDemoDb
Here “MySQLDemoDb” is our database name.
Now step by step, we learn about the SQL table and constraint.
Step 1. Here, we will create two tables (Parent and Child). We will create “tblMyEmployee” as the primary table and “tblMyDepartment” as the sub-table.
Sub table is used to reduce redundancy and complexity. Divining the large database table into smaller tables and linking them using relationships is helpful.
We use the “Create table” statement to create a new table in the database.
First, we will learn how to create the table in an SQL server. Run the below query for creating Employee and department table.
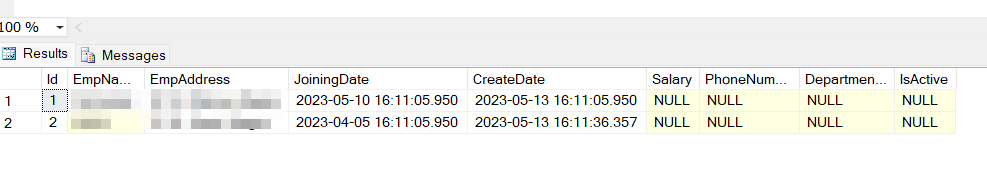
Create table tblMyDepartment ( Id int primary key identity(1, 1), DepartmentName varchar(50), IsActive bit ) Create table tblMyEmployee ( Id int primary key identity(1, 1), EmpName varchar(20), EmpAddress varchar(max), JoiningDate datetime, CreateDate datetime default( getdate() ), Salary decimal(5, 2), PhoneNumber varchar(10), DepartmentId int foreign key references tblMyDepartment(Id), IsActive bit )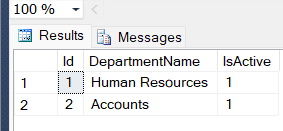
We add dome dummy data using insert Insert statement.
- The column parameters specify the names of the columns of the table.
- Here we see “varchar, int, decimal, etc.” these are the datatype. In SQL, datatype defines the type of data that column can hold (e.g. varchar, int, decimal, date, etc.).
We create Id as the “Primary key”.
- It is used for identifying each record of a table uniquely.
- The primary key column can’t be duplicated or null.
- We can only take one primary key in a table; this primary key can consist of single or multiple columns (ex., Primary key(ID) or Primary key(ID, EmpName, EmpAddress)).
Here DepartmentId we created as “Foreign Key”.
- It is a field or collection of fields in one table that refers to the “Primary Key” in another table. It is used to prevent activities that would destroy links between tables.
We used the “Identity” keyword to perform an auto-increment feature.
- The Identity keyword is used for auto-increment for records at the time of insertion in the SQL table.
- We used identity as “Identity(1,1)”; this means records start with 1, and it will increment by 1 after inserting every new record.
Step 2
The ALTER TABLE statement is used to add, delete, or modify columns or constraints in an existing table.
Here we are trying to add the EmailAddress column of datatype “varchar” with a size “50” charactor in the “tblMyEmployee” table.
To add a column in a table, use the following syntax,
Now we are deleting the “PhoneNumber” column from “tblMyEmployee”.
To delete a column in a table, use the following syntax
If we want to change the data type of the existing column, then we use the below query.
Here we are changing the datatype of “PhoneNumber” to “nvarchar” with size “10”.