Understanding Parallel.ForEachAsync vs Task.WhenAll in .NET
Parallel is one of two popular alternatives in.NET when handling many objects at once. Both Task and ForEachAsync. WhenEverything. Although they both execute work in parallel, their approaches to concurrency management differ, and this can have a significant impact on performance. Let’s examine each one’s operation and contrast it with an actual case.
Parallel.ForEachAsync: Controlled Parallelism
Parallel.ForEachAsync (introduced in .NET 6) provides built-in throttling via MaxDegreeOfParallelism. It schedules work intelligently, without creating a separate task for every item.
Example
Key Idea
Runs only a limited number of iterations in parallel — typically one per CPU core.
Task.WhenAll: Fire-and-Wait for All Tasks
Task.WhenAll simply runs all tasks at once and waits until every one of them completes.
Example
Key Idea
Starts one task per item, no throttling — great for small workloads, but dangerous at scale.
Custom Throttled: Task.WhenAll – using SemaphoreSlim to limit concurrency for async workloads
Observations from Your Benchmark
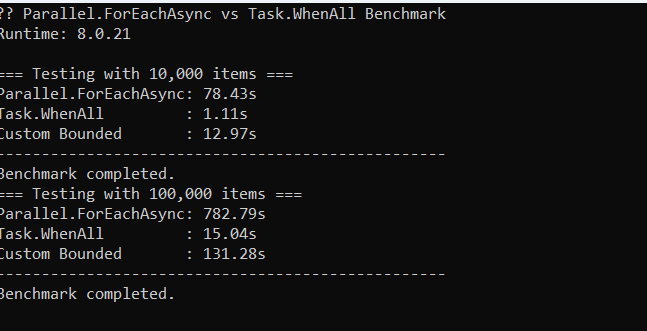
| Method | 10,000 items | 100,000 items | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel.ForEachAsync | 78.43s | 782.79s | Very slow because concurrency is limited to Environment.ProcessorCount (e.g., 8). Great for CPU-bound tasks, but for async I/O it’s throttling too much. |
| Task.WhenAll | 1.11s | 15.04s | Extremely fast because all 10K or 100K tasks run concurrently. Ideal for async I/O. Memory usage is high but delay is very small. |
| Custom Bounded (SemaphoreSlim) | 12.97s | 131.28s | Middle ground. Controlled concurrency (e.g., 50 tasks at a time). Prevents thread pool overload while still allowing high concurrency. |
Why the Numbers Look This Way?
- Parallel.ForEachAsync
- Limited by MaxDegreeOfParallelism = CPU count (~8 on most machines)
- Each task waits 50ms (simulated I/O) before completing
- So 10,000 / 8 × 50ms ≈ 78s — matches your result
- Task.WhenAll
- Launches 10,000 tasks immediately
- Task.Delay is non-blocking → tasks don’t consume threads
- Finishes in ~1s (10K) and 15s (100K)
- Custom Bounded
- Limited concurrency (50 in your example)
- 10,000 / 50 × 50ms ≈ 10s — matches closely (12.97s)
- 100,000 / 50 × 50ms ≈ 100s — matches closely (131.28s)
Key Takeaways
- CPU-bound tasks → Parallel.ForEachAsync wins
- Async I/O tasks with thousands of operations → Task.WhenAll is fastest, but can risk memory pressure
- Large async workloads with controlled concurrency → Custom SemaphoreSlim approach is safest
Note: Adjust maxDegreeOfParallelism in your custom method depending on CPU cores and I/O type
Conclusion
Task.WhenAll continuously performs better than Parallel. The difference between ForEachAsync and the custom bounded solution is substantial, particularly when the number of objects rises. Because to its limitless concurrency and overhead every iteration, Parallel.ForEachAsync performs the poorest. By restricting concurrency to lessen resource competition, the custom bounded approach provides a compromise that outperforms parallel. Task is still faster than ForEachAsync. WhenEverything. In this case, Task.WhenAll is the most effective method for high-concurrency async operations.
Have fun with your coding!
ASP.NET Core 10.0 Hosting Recommendation
HostForLIFE.eu
HostForLIFE.eu is a popular recommendation that offers various hosting choices. Starting from shared hosting to dedicated servers, you will find options fit for beginners and popular websites. It offers various hosting choices if you want to scale up. Also, you get flexible billing plans where you can choose to purchase a subscription even for one or six months.

